Java Lambda Expression - Aggregation
A lambda expression is an anonymous function which performs arithmetic or relational operation over an array of data in sequential or parallel manner. It replaces for-loop like operation over array objects.
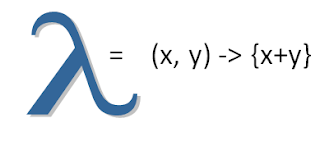 |
| lambda expression |
Stream Object The array of data might be a java primitive data type (integer or long or double) or a java collection object (ArrayList). In order to execute the lambda expression over array of data, we need a Stream object (IntStream, LongStream or DoubleStream).
The Stream object can be obtained by many ways, however, an example shown here.
An array variable X initialized with random integers
int X [] = { 48, 21, 23, 45, 53,
14, 18, 34, 11,
19,21,23,53
};
IntStream object is obtained by passing X as a argument
to Arrays.stream function.
IntStream intstream =Arrays.stream(X)
An array variable X2 initialized with random integers
double X2 [] = { 0.58, 2.1, 1.23, 0.45, 3.57,
5.62, 0.86, 0.234, 0.361,
0.296,0.211
};
DoubleStream object is obtained by passing X2 as a argument
to Arrays.stream function.
DoubleStream dblstream =Arrays.stream(X2)
The obtaining Stream object depends on
type of argument passed over Arrays.stream.
The Stream object's member functions support the following application over array of data using lambda functions, They are,
- Aggregation
- Filtering
- Maping
- For Each
Lambda expression Aggregation over array of interger
The following Java code shown below is example of lambda expression application over on array of integers, generated randomly using the Random object. The lambda aggregation functions like
sum - sum over an array elements,
average - average over an array of elements
min - find a element have minimum value
in the array of elements
max - find a element have maximum value
in the array of elements
it results one element output given over array of elements
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Lambda1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int size=20;
int X [] = new int[size];
Random rd = new Random();
for (int n=0;n<size;n++)
X[n] = rd.nextInt(100);
System.out.println("\n A randomly integer array ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(X));
System.out.println("\n Find sum of the array ");
IntStream ints=Arrays.stream(X);
int sum = ints.sum();
System.out.println("sum :"+ sum);
System.out.println("\n Find Average of the array ");
IntStream ints2=Arrays.stream(X);
double average = ints2.average().getAsDouble();
System.out.println("Average :"+ average);
System.out.println("\nFind Maximum of the array ");
IntStream ints3=Arrays.stream(X);
int max = ints3.max().getAsInt();
System.out.println("Max :"+ max);
System.out.println("\nFind Minimum of the array ");
IntStream ints4=Arrays.stream(X);
int min = ints4.min().getAsInt();
System.out.println("Min :"+ min);
}
}
Output
A randomly integer array
[33, 87, 30, 62, 47, 46, 93, 12, 37, 24, 38,
67, 15, 94, 39, 21, 89, 35, 83, 48]
Find sum of the array
sum :1000
Find Average of the array
Average :50.0
Find Maximum of the array
Max :94
Find Minimum of the array
Min :12





Comments
Post a Comment